- Marketers Guide
- Getting Started
- Setting Up Attribution
Attribution Methods
Airbridge collects touchpoint and conversion data to reconstruct the user journey and measure ad performance.
Given the complexity of user journeys spanning various platforms and devices, Airbridge uses several attribution methods to ensure accuracy.
A user journey consists of a series of user interactions with advertisements and the resulting business outcomes. The ad interactions are referred to as touchpoints, and the business outcomes as conversions.
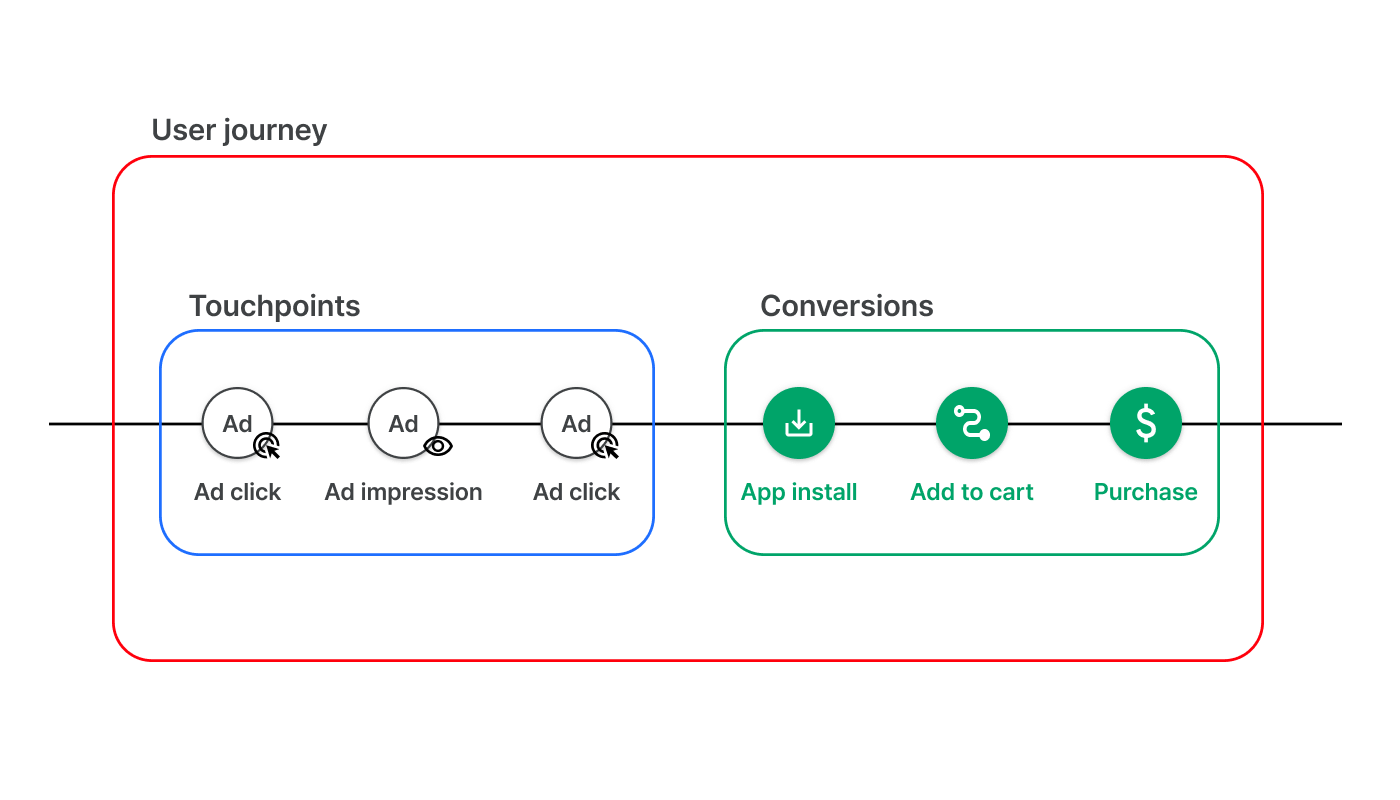
Airbridge reconstructs user journeys using multiple attribution methods while employing 2 major approaches: the deterministic and probabilistic approach.
The availability of identifiers varies depending on the platform. For the comprehensive management and use of multiple identifiers, Airbridge has implemented the Airbridge Device ID.
Airbridge Device ID
Airbridge Device ID is a Universally Unique ID used to identify devices. As a default, GAID for Android and IDFA for iOS are used. If GAID or IDFA is unavailable due to LAT (Limited Ad Tracking) or ATT (App Tracking Transparency), IDFV or a randomly generated value is used instead.
The deterministic approach relies on verifiable information to attribute a conversion directly to a specific touchpoint.
Airbridge uses device IDs to connect clicks to installs. Available device IDs include IDFA and IDFV for iOS, and GAID for Android.
In addition to device IDs, Airbridge can collect cookie IDs while redirecting users to an app store. When a user clicks on an in-app ad, the Airbridge tracking link used in the ad will collect the device ID of the user. Then, when the user is briefly sent to a webpage called “Airpage” before being redirected to the app store, Airbridge collects the cookie ID of the user.
For ad campaigns on self-attributing networks (SANs), such as Meta Business, Google Ads, and Apple Search Ads, Airbridge uses identifiers provided by the SANs for attribution.
Tracking links are not used to measure campaigns on SANs, but whenever an app install occurs, Airbridge requests the SANs to send the touchpoints that may have driven the install. Airbridge uses the identifiers provided by the SANs for attribution.
SKAdNetwork (SKAN) is Apple’s privacy-centric attribution framework for iOS devices. SKAN allows for app install measurement without user or device identifiers. Airbridge supports SKAN in parallel with other attribution methods.
For more details on SKAN, refer to this article.
The user may have already installed the app on the device. In this case, upon clicking on a deep link-embedded ad, the user is directly sent to the app without landing on an app store. This allows Airbridge to connect the click directly to the app open using the information collected with the deep link.
Deep linking can be used for re-engagement attribution.
Install referrer matching is performed using the information carried by the install referrer to attribute installs. This method is available for Android only.
Note
When install referrer matching is used for attribution, Airbridge cannot determine the exact time of the touchpoint occurrence because it is unable to collect the timestamp of the touchpoint data. As a result, Airbridge assumes that the touchpoint occurred 1 hour prior to the install event. This assumption applies to all ad channels.
Here is how the install referrer matching works for attributing installs:
A user clicks on an ad to download your app from the Google Play Store.
Airbridge sends a referrer with the user's web ID to the Google Play Store.
When the user opens the app for the first time after install, the install referrer is passed to Airbridge with the user's web ID and app ID. With this information, Airbridge can perform user matching for attribution.
Note that Meta also supports its own install referrer designed to attribute Android installs to Meta ads. For more information about the Meta install referrer (MIR), refer to this article.
The probabilistic approach is used when no deterministic identifiers are available. Airbridge prioritizes the deterministic approach over the probabilistic approach for user identification.
Airbridge uses probabilistic modeling to infer the connection between touchpoints and conversions within a 6-hour timeframe.
Additional attribution rules and machine learning-driven statistical modeling are used.
Certain Airbridge features use statistical inference based on data collected via tracking links, such as the device model, OS name, and app ID.